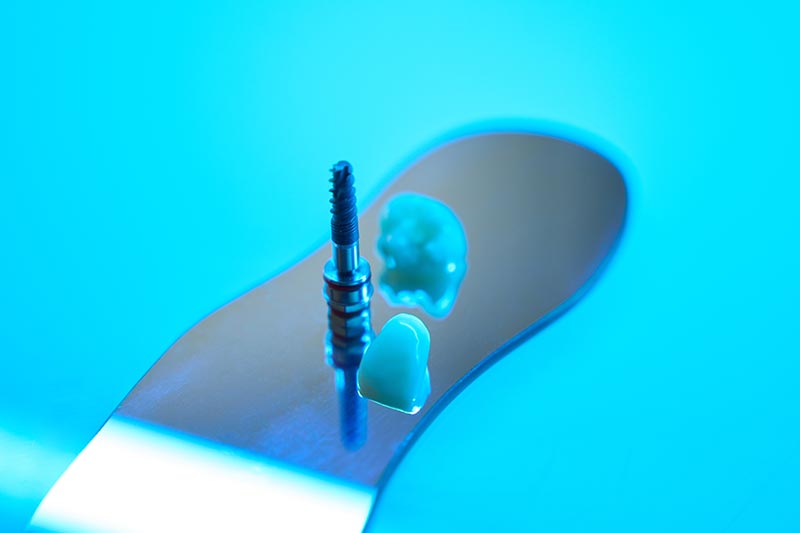
The purpose of dental implants is equivalent to that of natural tooth roots. They are fixed components placed in the jaw that serve as support and anchorage for the prosthesis used to replace one or more missing teeth.
Today, the most widely used material for manufacturing dental implants is titanium.
Why is titanium used for dental implants?
There are several reasons to consider titanium the ideal material for dental implants. Chief among them are its excellent biocompatibility which prevents rejection by the body and its ability to bond to bone in a process called osseointegration, allowing the implant to remain stable and immobile.
Titanium’s biocompatibility, combined with its mechanical properties hardness, lightness, and strength has enabled numerous medical applications of great value, such as hip and knee prostheses, as well as heart valves and pacemakers.
Titanium also has high resistance to oxidation and other chemical processes, making it one of the most corrosion-resistant metals.
How are titanium dental implants placed?
Placing a titanium implant typically involves two phases: the surgical and the prosthetic phase.
- Surgical phase: The titanium implant (screw) is inserted into the bone, where it will act as an anchor for the future prosthesis. Dental-implant surgery is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia.
- Healing & osseointegration: The healing and osseointegration period usually lasts 3 to 4 months. During this time, the patient may use temporary prostheses.
- Prosthetic phase: Once the implant has fused to the bone, it is uncovered and a healing abutment is placed so the gum doesn’t cover it again. After two weeks, the dental specialist takes an impression to create the new teeth. Posts/abutments are connected to the implant, and the crowns are placed on top.
Can titanium dental implants cause allergy or rejection?
Thanks to titanium’s excellent biocompatibility, it is very rare for titanium dental implants to cause an allergic reaction or be rejected by the body.
What can occur is insufficient osseointegration, meaning the bone does not bond adequately to the implant to keep it stable in the mouth.
This lack of osseointegration can be due to technical issues during surgery, postoperative complications, or patient-related factors such as poor oral hygiene.
What other materials are dental implants made of?
Dental implants are also made of zirconia, a ceramic material of exceptional hardness and strength used for manufacturing bridges and crowns. Its white color closely resembles natural teeth and it has excellent durability.
Zirconia implants bond to bone through biointegration, a chemical union that forms a layer at the interface between the bone surface and the implant surface.
Despite their advantages, there are fewer long-term studies on zirconia’s durability, and on its use in full-arch rehabilitations.
Zirconia implants are not recommended for immediate loading (placing screwed-in or cemented teeth the same day as surgery) and are generally more expensive.
This informational post describes titanium and zirconia implants. While both materials have benefits, titanium has more long-term evidence and is the most widely used. The right choice of material and technique depends on each individual case. This text does not replace a diagnosis; determining the best solution for you requires a clinical evaluation.
Restore your smile with the safety and durability of titanium implants. Schedule a consultation. Contact us via WhatsApp, phone, or through our online form.