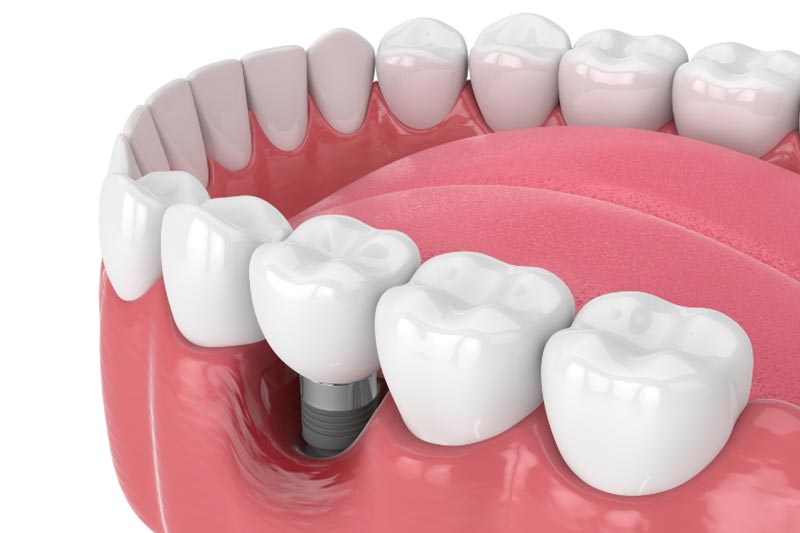
Dental implants are among the most important advances in modern dentistry. They greatly improve patients’ quality of life by restoring oral function and the esthetics of their smile.
Because implant placement is a minimally invasive procedure, outcomes are highly predictable with a high success rate as long as treatment is performed by a specialist. However, implants can develop complications if the required care is not followed.
The main problems that can affect dental implants are known as peri-implant diseases.
Peri-implant disease is an inflammatory process that affects the tissues (gum and bone) surrounding a dental implant. It can cause a loss of the bone support into which the implant has integrated.
There are two grades of peri-implant disease:
- Mucositis: Similar to gingivitis, but around implants. It is characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the tissues surrounding the implant.
- Peri-implantitis: Similar to periodontitis, but around implants. It is characterized by bone loss around the implant.
What are the symptoms of peri-implantitis?
- Redness of the tissues surrounding the implant.
- Bleeding.
- Pain in the área.
- Bone loss in the supporting bone.
- Implant exposure (threads becoming visible).
What causes peri-implantitis?
- Periodontal disease.
- Low bone volume: over time, bone around the implant can be lost, exposing the implant threads.
- Poor oral hygiene: one of the most influential factors, since it allows bacteria to colonize the implant Surface.
- Improper implant placement: which is why it’s essential to be treated by an experienced specialist.
- Deficient implant rehabilitation (prosthetic work).
What are the risk factors for the development of peri-implantitis?
- Smoking.
- Thin gingival biotype (thin gums).
- Poorly designed implants.
- Poorly controlled diabetes.
What is the treatment for peri-implantitis?
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease and may include:
- Resective treatment: removal of diseased tissues plus cleaning and disinfection of the implant Surface.
- Regenerative treatment: elimination of the infecting bacteria to reduce inflammation and regenerate lost tissues.
- Implant removal: when previous approaches do not offer predictable medium- or long-term results.
To prevent peri-implantitis, prevention is the most effective strategy. Follow all instructions from your implant specialist, maintain excellent oral hygiene, and attend regular checkups to ensure your implants remain in good condition.
This article explains what peri-implantitis is and emphasizes that prevention is the most effective strategy. Long-term implant success depends both on good oral hygiene and on periodic visits with a specialist. This content is informational; to receive a maintenance and care plan for your implants, a professional evaluation is required.
If you notice bleeding, inflammation, or any discomfort around your implants, don’t wait. Book an evaluation. Contact us via WhatsApp, phone call, or through our form.