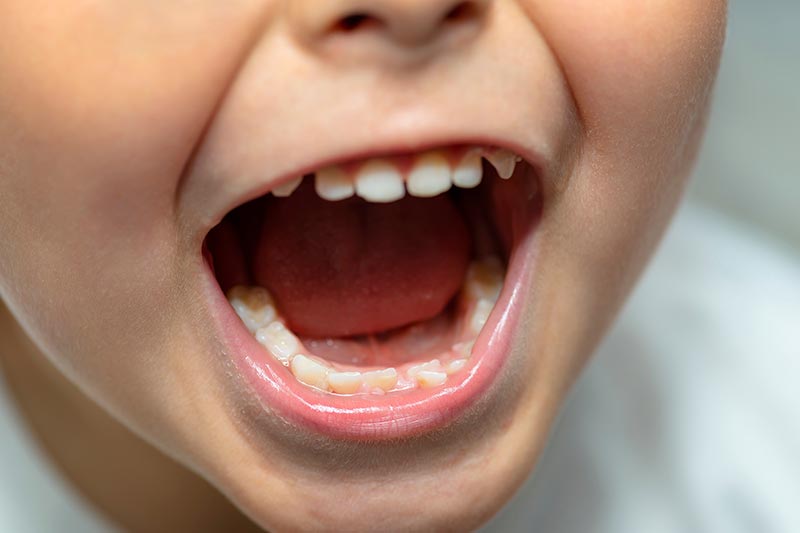
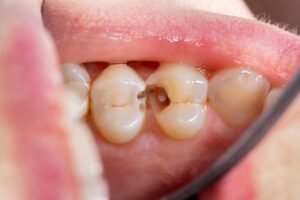
Although temporary, baby teeth (primary teeth) play a very important role in a child’s development. Caring for them well helps prevent future oral problems.
The first teeth usually appear around 6–7 months of age, and the last ones erupt between 2 and 3 years. During this period, 20 primary teeth emerge preparing the way for the 32 permanent teeth of adulthood. Primary teeth begin to be replaced by permanent teeth at about 5–6 years of age.
Baby teeth fall out due to the pressure from the developing permanent teeth underneath. First, the child notices a slight wiggle, which increases until the tooth finally falls out. In some cases, permanent teeth can erupt before the primary teeth have fallen out a situation commonly called “shark teeth.”
What are the functions of baby teeth?
- Feeding: Good digestion begins with chewing. Baby teeth help children break down food, and chewing also strengthens the oral muscles.
- Speech: Primary teeth aid coordination between the tongue and lips, supporting clear pronunciation.
- Jaw development: Chewing stimulates jaw growth. Even very young babies instinctively practice this when they bite their toys.
- Space maintenance for permanent teeth: Premature loss of baby teeth can cause space problems later on.
How should baby teeth be cared for?
Oral hygiene starts even before the first tooth erupts. Keep the gums clean so healthy primary teeth can emerge later. After each feeding, gently wipe the gums with a damp cloth.
Between ages 1 and 2, when most baby teeth are in, switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush and clean with water at least twice a day. Starting at one year, children can begin visiting a pediatric dentist.
From age 3, children should see the pediatric dentist more regularly and begin using a fluoride toothpaste appropriate for their age. Around age 6, you can introduce dental floss.
It’s important to teach and supervise good habits early. Watch their brushing until about age 8, or until they show enough independence and proper technique.
What commonly causes problems in baby teeth?
- Bottle: Always supervise bottle use. Don’t let children sleep with a bottle, as milk can pool in the mouth and lead to cavities.
- Pacifier and thumb-sucking: Prolonged use can affect tooth alignment. Keep pacifiers clean and never dip them in honey or sugar water.
- Sugary foods: High sugar intake favors cavities. Having decay in baby teeth significantly raises the risk of cavities in permanent teeth.
Good care of baby teeth supports the proper development of the permanent dentition. Besides preventing future complications, it helps your child keep a beautiful smile from an early age.
This information is for guidance. Cavities in baby teeth increase the likelihood of cavities in permanent teeth regular checkups are important.
For your child’s first dental checkup, contact us to schedule an appointment.